Perspectives
From Diagnosis to Treatment: Unlocking Potential with Generative AI
The healthcare industry stands at a pivotal moment. Facing complex challenges including labor shortages, clinician burnout, declining profitability, and low satisfaction, healthcare stakeholders are eager for solutions that can improve efficiency and effectiveness. During this time of heightened strain, generative AI presents a transformative opportunity. Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that can create new content and ideas, including text, images, audio, code, etc. based on patterns learned from large datasets.
The technology gained significant momentum in 2024, with advancements in large language models capturing widespread attention across industries. Publicly available models, like ChatGPT and Claude, have enabled broad mainstream uptake of these solutions. As of February of 2025, OpenAI has reached over 400M weekly active users, and over 45% of the U.S. population is using generative AI.
As a result, healthcare companies are beginning to recognize the importance of incorporating generative AI into their services. With administrative spending amounting to 15-30% of total U.S. healthcare spending, generative AI is poised to enhance efficiency and reduce cost by addressing critical pain points – from excessive administrative burden to fragmented patient journeys. One estimate indicates that AI could create $370 billion in additional value for healthcare companies. This value is recognized by all major healthcare stakeholders – payers, providers, life sciences, and med-tech companies – who are now strategizing how to deploy and implement AI into their workflows. (See “Generative AI Buyer Segments” for more detail)
Reflecting this trend, the digital health market has prioritized start-ups with a generative AI component in their value proposition, with 37% of 2024’s digital health funding going to AI-enabled companies. Despite enthusiasm for generative AI, the technology is still in an experimental phase for most healthcare stakeholders. While 70% of healthcare companies plan to use generative AI, only 30% have fully implemented solutions. Given the technological and financial barriers to developing generative AI solutions, most companies are turning to third party partnerships to deploy pilots.
While the applications of generative AI in healthcare are vast, healthcare stakeholders believe it holds the most potential in clinician productivity and consumer experience. To fully realize these benefits, establishing trust with providers and consumers is critical. As of 2024, 37% of consumers use generative AI for health reasons and 53% would trust generative AI to diagnose conditions. However, consumers have tangible concerns regarding the technology. In 2024, 30% of consumers reported distrusting health information derived from generative AI, up from 23% in 2023. Providers shared similar mixed feelings. Physicians are particularly concerned about potential efficacy and regulatory concerns surrounding the technology. At the same time, they are optimistic about its potential role in improving care, with 56% of providers believing AI will be helpful in improving care coordination, patient convenience and patient safety.
A comprehensive and reliable regulatory framework will be critical for establishing trust and paving the way for clear reimbursement. While the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and the House Bipartisan Task Force on AI have released reports on AI’s role in healthcare, no significant federal legislation has been introduced. Given minimal federal guidance, states are working independently to pass legislation on AI’s role in healthcare. To date, 100+ health related AI bills have been introduced across 34 states. This has resulted in a patchwork landscape and unclear path for firms innovating in this space.
To fully unlock the potential of generative AI in healthcare, overcoming regulatory uncertainty and building trust will be just as critical as technological advancements. Beyond administrative efficiencies and clinician productivity, AI is set to redefine care delivery and consumer engagement. AI-powered solutions can enhance diagnostic accuracy, personalize treatment pathways, and predict health risks with unprecedented precision. As AI adoption accelerates, companies that successfully integrate AI into their offerings – while addressing trust concerns and ensuring compliance – will be well-positioned to drive the next wave of digital health transformation. Those that fail to do so risk being left behind in an industry increasingly shaped by intelligent automation and data-driven insights.
Stakeholder Priorities & Partnerships in Generative AI
Facing high technological and financial barriers to entry, healthcare stakeholders are turning to partnerships to advance their AI strategy. Today, only 24% of healthcare companies are building generative AI capabilities in-house. We expect that generative AI deployment in healthcare will be driven by platform players (e.g., OpenAI, AWS) supplying the underlying LLMs and infrastructure, while healthcare companies build specialized offerings on top of this foundation.
Key healthcare stakeholders include:
- Employers: Employers are interested in solutions that simplify the healthcare experience, from consumer education to care navigation. U.S. adults spend 8 hours per month coordinating healthcare for their families. To address this, Transcarent, a 7wire portfolio company, has introduced WayFinding – a tool leveraging generative AI to create a personalized experience for benefits navigation, clinical guidance, and more.
- Pharma: Pharmaceutical companies are accelerating drug discovery and development – from molecular design to trial enrollment. Sanofi entered a $1 billion strategic collaboration with BioMap, an AI-driven life sciences startup, to streamline biotherapeutic drug discovery.
- Providers: Providers are engaging solutions that reduce administrative burden and support clinical decision making. Corewell Health has partnered with Abridge to implement its AI platform for clinical documentation, which will be offered to approximately 4,000 clinicians across sites of care. Abridge has been deployed in more than 100 health systems and recently announced its $250M Series D.
- Payers: Payers are streamlining member communications including member materials, phone calls, and summarizing member interactions. Highmark Health is partnering with Google Cloud to develop generative AI solutions that streamline content creation, personalize member materials and summarize calls.
- Medical Technology: Med Tech companies are incorporating AI to support clinical decision-making, improve diagnostic accuracy, and automate administrative tasks. Philips is partnering with AWS to add generative AI tools to its HealthSuite Imaging platform.
- Big Tech: Big Tech firms are leveraging their expertise to create healthcare-specific LLMs and tools. Microsoft has partnered with Epic to rapidly deploy dozens of AI powered “copilot” tools, integrated into Epic’s EHR system, which will assist clinicians by automating tasks such as medical note summarization, coding and billing, among others.
Generative AI in Healthcare Landscape
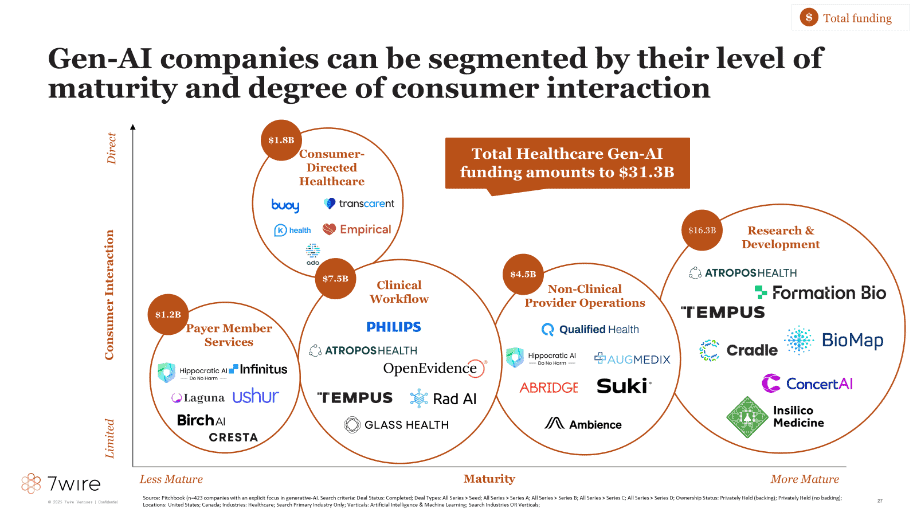
Healthcare focused generative AI solutions can be segmented across 5 key categories: non-clinical provider operations, payer member services, consumer directed healthcare, clinical workflow, and research and development. We’ve identified ~$31.3B in total healthcare generative AI funding to date across these 5 segments.
Non-Clinical Provider Operations ($4.5B): Generative AI is being used to automating non-clinical workflows, allowing providers to spend more time with patients. Applications include documentation, revenue cycle management, simple patient interactions, scheduling, and more. Summer Health, a 7wire portfolio company, partnered with OpenAI to create its medical visit notes feature, which uses GPT-4 to generate visit notes, reducing time spent on administrative tasks by 5x. Hippocratic AI is one of the front-runners in this space, growing rapidly in just the past few months. Their platform offers a “staffing marketplace”, enabling health systems, payers, and others to hire generative AI powered agents to conduct low-risk, non-diagnostic, patient-facing services.
Payer Member Services ($1.2B): Generative AI is poised to overhaul the way health insurers deliver member services, including patient communications, claims operations, prior authorizations, and fraud detection. Payers see generative AI as a means of driving greater efficiency, reducing MLR, and allowing resources to be re-focused towards new capabilities and services. For instance, Infinitus Systems enables automated payor and PBM data collection through digital AI copilots and voice-powered AI agents, culminating in their latest $51.5M Series C in October, 2024.
Consumer-Directed Healthcare ($1.8B): Generative AI can empower consumers to take charge of their own healthcare, which is closely aligned with our thesis at 7wire Ventures. Generative AI can streamline the healthcare journey by providing personalized care navigation, unifying patient records for seamless consumer access, and enabling symptom checks through AI-powered chatbots. K Health is an AI-driven primary care company aiming to make high-quality medical care accessible through its 24/7 virtual primary care mobile app, which features an AI-chatbot to facilitate connections to doctors for further consultation.
Clinical Workflow ($7.5B): Generative AI can enhance clinical workflows, extending a constrained provider supply and reducing burnout. Despite this allure, generative AI has yet to substantively penetrate clinical workflows. A key factor is provider resistance, as liability around patient care is greater, requiring a high bar of evidence and validation. Additionally, uncertain regulatory and reimbursement pathways have constrained adoption. That said, some companies are innovating here. Rad AI’s flagship product, Omni Impressions, utilizes generative AI to automatically generate reports after a radiologist dictates the raw findings. OpenEvidence offers a provider copilot that aggregates and analyzes clinical research to provide tailored insights and recommendations to improve the accuracy of diagnoses and treatment plans.
Research & Development ($16.3B): Life sciences companies are using generative AI to make the drug development process more efficient, for example in generating real world evidence and accelerating clinical trial recruitment. For example, Atropos Health specializes in generating real-world evidence using AI-powered solutions. Their chat-based AI co-pilot, ChatRWD, enables users to quickly generate publication-grade RWE studies using generative AI, supporting clinicians, life sciences companies, and researchers. Furthermore, Sanofi, Formation Bio, and OpenAI have developed Muse, a tool aimed to expedite clinical trial recruitment.
Generative AI & Our Informed, Connected Health Consumer Thesis
Generative AI is poised to super-charge digital health companies that align with 7wire Ventures’ Informed, Connected Health Consumer thesis. These partnerships enable digital health companies to build powerful capabilities that drive step improvements in patient care, from personalizing patient care to automating clinical documentation. We’ve identified 6 sub-categories that illustrate how generative AI is transforming the consumer healthcare journey:
7wire Ventures Predictions
- Generative AI will increase its share of search, providing consumers with more informed answers to their health questions. As leaders like OpenAI and Anthropic continue to deliver rapid advancements in LLMs, consumers will seek tools like ChatGPT as first-stops for health-related questions, rather than traditional tools (i.e., Google, WebMD). Generative AI will provide consumers with real-time health insights based on patient data, answering medical questions relating to their healthcare status, and more. Access to timely medical information without requiring a physician visit will enhance access to care and reduce cost.
- While investment will grow in both clinical and non-clinical applications, practical utilization of generative AI will center upon non-clinical areas for the foreseeable future, as doctors remain concerned with reliability and personal liability for use of these tools. Without additional data demonstrating efficacy of generative AI tools, clear references about how AI decisions are made, and stronger regulatory guardrails regarding the technology, physicians will continue clinical practice according to status quo. Given the current federal political landscape, we expect a more laisse-faire approach to generative AI regulation, requiring states to continue to build individualized guardrails regarding proper use of this technology. Agentic AI will support provider adoption of non-clinical applications, automating tasks related to intake/triage, care management, billing / claims, customer support, and more – saving both time and money for health systems and patients alike.
- Health plans, PBMs, and pharmaceutical companies will find significant savings from use of generative AI for tasks that previously required considerable time and expensive resources (i.e., back office functions). Given how nascent generative AI technology is, organizations have struggled to quantify ROI – we expect increasing confidence in positive ROI as the technology is leveraged for more large-scale applications. Health plans will realize greatest value from generative AI by incorporate tools to support care navigation, member services, and back-office functions (i.e., claims, billing, eligibility) – areas that can largely be automated through agentic AI. Pharmaceutical companies will provide incremental value to consumers by using generative AI to support more personalized adherence programs, enabling consumers with tools / resources to better understand their medications, treatment plans, and answer prescription-related questions.
As generative AI continues to evolve, its impact on healthcare will extend far beyond automation – it will fundamentally redefine how care is delivered, accessed, and experienced. Companies that embrace AI strategically – leveraging partnerships, ensuring transparency, and aligning with the needs of providers and consumers – will be best positioned to thrive in this new era of digital health. As we look ahead, generative AI is not just a technological breakthrough; it is a paradigm shift that has the power to drive meaningful, lasting improvements in healthcare efficiency, affordability, and outcomes.